Invent the Future editor Carlos Martinez interviews Li Jingjing, a Chinese journalist who covered the Covid outbreak in Wuhan for CGTN, about China’s coronavirus containment efforts. We discuss the current situation in China, the measures that have been taken to eliminate the virus, the broad mobilisation throughout China to help the people of Wuhan, the need for international cooperation to defeat the pandemic at a global scale, and more.
Transcription highlights
Our friends at ChinaSquare have transcribed some highlights from the interview in order to publish them in Dutch. Below you can find the English version.
So how is the situation in China now in terms of the pandemic?
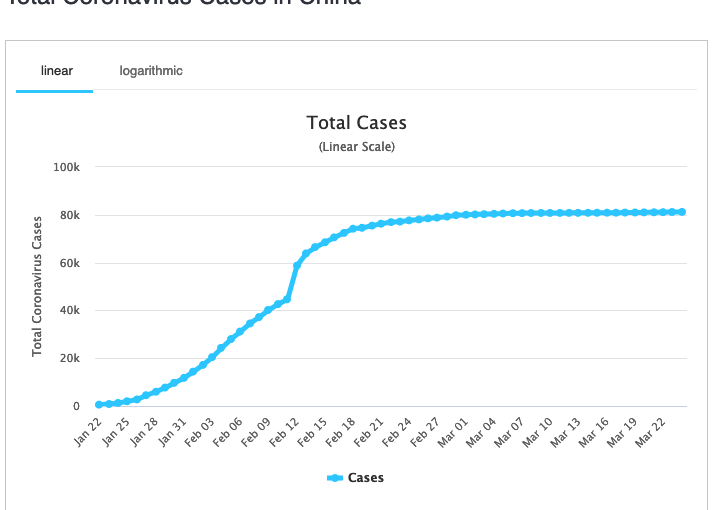
Since May everything got back to normal everywhere. Recently, there have been some cases popping up in different provinces in China. But the government responded very fast. When there were five cases in a certain district, the next days they tested over 1.2 million people in that place. They found almost all close contacts, and put them into isolation centres for observation.
So as soon as there’s a case detected, then everyone is tested and they do the contact tracing and the isolation?
Early in the year people were still trying to figure out what’s the best method to do it. But now I think every city and every province has already got this format, how to deal with it. Anyone who was just potentially a tiny bit exposed to the virus, gets tested and treated.
And people are using the QR code system then? And that’s normal now?
Yes, they started to do that in Wuhan. It is like what we use for WeChat, or Alipay. They have different colours, green code, red code, and yellow. Green code basically means you were never exposed, not having contacted anyone who has exposed and you have never been to high-risk regions. So as long as you have a green code, you can go anywhere you want. Red code means that you were probably infected or exposed, or maybe you went to a high-risk region. Basically now, because of the new cases, everywhere we go, we have to scan this QR code. A restaurant will have my information, if they suddenly find some cases, they will be able to contact all the customers who went there. So that’s why we register, not for surveillance or something like that.
And how difficult is it to get tested? Do you have to travel a long way to do that? Does that cost money? Can you do it quickly? How long would it take to get the results?
You can just go to the nearby hospital, get tested, and get the result within 24 hours. But if there’s an outbreak they’re testing the regions where the new cases showed up. There they show the results within six hours. So that can be very, very fast.
And how long has all this infrastructure been in place? Was that put in place quite early into the initial outbreak?
Once they lifted the lockdown, people were going to shopping malls, to public places. Then this new system was put in place. In April or in May everybody in all provinces started to use this.
Could you tell us about why you were in Wuhan? What you did during the lockdown? What was the atmosphere like there in the city? How did people handle that?
I’m a reporter, so when I heard there was an outbreak, of course, I was scared, but my response was I want to go there to see what’s happening, I want to cover the story. So my boss allowed me to go. I went to Wuhan in February. I stayed there for 73 days and came back late April. To be honest, during that time, things were quite scary. Not just in Wuhan, but in general in China. Everybody knew there was unknown pneumonia, and there was the Spring Festival. So everybody was supposed to go home and be united with their family and suddenly there was this lockdown. Only a few people could move around. So occasionally you could see an ambulance, taking patients to hospitals, you could see people in protective suits on the street, transporting patients, or delivering food and necessities to different households. As a reporter I went to different hospitals, I interviewed a lot of nurses, doctors, patients, and those who just basically volunteered to do the job to deliver food for different communities and households. I was lucky to witness the entire process, how things got so scary in the beginning, and then how the people really got together to fight everything, and things gradually getting back under control.
I think one of the things that here in the West, we found really difficult about lockdowns is the lack of support going to disadvantaged people who haven’t been able to get the level of support that they would normally have. And we saw that in India as well. In China, how have those situations been dealt with?
Putting a strict lockdown doesn’t mean you’re just isolating this region entirely. Wuhan was trying to snap this transmission chain, so the virus would not go to other places. But they were providing all kinds of support to everybody. This highlights the importance of neighbourhood committees. Because in this kind of committee, probably 20 or 30 people were taking care of thousands of households, buying and delivering food. They went to every door to check different situations of each family. Some families have patients with other diseases, or those who have to go to hospital regularly. Most of the neighbourhood committee members are CPC members. They are just ordinary people who were working non-stop 24/7, during those three months of tough lockdown. The local people love those CPC members.
It is the Chinese way. In the West people are still debating whether they should wear a mask, but here this is a no-brainer. All of us know we have to wear a mask. We do not want to infect others and do not want to be infected. Everybody knows how to disinfect. When Wuhan was under lockdown everybody was trying to help inside the city, but also from outside the city. Top medics came from different provinces. Provinces donated the products, the food they are famous for or specialize in.
So in spite of what obviously was a very difficult situation, everybody had food, people had their medicines. When people needed dialysis or hospital treatment, they received that.
And you can compare that with the situation in New York City, where those kinds of people were queuing down several blocks on the street to get food from food banks
Yeah, here in China, you will get everything because some people will provide all those things to your door. And I just remember one story about a person in need of special treatment. I interviewed this Uyghur guy from Xinjiang. He had gone to Wuhan to do this kidney transplant. And so before the lockdown, he had just finished his surgery and had just got a new kidney. So he needed a lot of intensive care. He said: ‘community workers came to my door and knew my situation.’ Even though it was so difficult for them to manage that, they made sure to arrange whatever check was necessary. During that time one of his doctors just picked him up every day and took him to hospital to do certain checks and whatever he needed. He’s old, but he recovered from everything and has still got everything. He is from Xinjiang, but he says: ‘Wuhan is my second home, because they gave me a second life’. And he’s a Uyghur and a CPC member. This a true story.
China was able to send tens of thousands of doctors and other medical staff to Wuhan, more or less at a moment’s notice, and to build these incredible facilities, modern, fully equipped hospitals in a matter of a few days. How was it possible to mobilize resources at that scale so quickly?
This kind of thing is always possible here. In each province the government asked doctors and medics. Most doctors said: ‘of course I will go’. They said: ‘that’s our responsibility as a doctor, this is the place I need to go to. I’m not thinking of getting gratitude from the citizens. If I’m a doctor, and I’m not going, I will regret this for my entire life’.
In terms of how is it possible? I think maybe it’s really a very effective government. They’re able to work out an effective method within a very short time, with the best resources, the people or food, everything. They centralize resources and send them to the places where they’re most needed.
I think the incredible solidarity that people showed from different parts of China really runs against the stereotype that people have in the West about China and Chinese people. They think it is a strict authoritarian society, where Xi Jinping and the Communist Party tell everyone else what to do. And everyone else is just like robots and they hate their lives. So this idea of solidarity and not being motivated by material rewards, but by very human sentiments definitely goes against the stereotypes about China.
I think it’s never a problem for people here. We always think we should be united especially during this tough time. I think unity, helping each other is much more important than individualism. When my friends and I read in the news that some people are shouting: ‘I’m not going to wear a mask, because it’s my freedom, I was born in a free land’, we think: ‘your freedom is jeopardizing other people’s freedoms. Because of that individualism you will never get back to normal. Is that what you want?’ So I think here in China, we really value this collectiveness. One nurse, she was working eight hours every day in this makeshift hospital. She was providing more than medical checks, psychological treatment of the patients. After things got better and patients were healed, she could go back home. And she chose to stay, saying: ‘there are still severely ill patients in hospital. I need to go to ICU to help those patients.’ When the whole thing was finished, she had a health check and it was found that she had cancer, so she had put herself in danger, that was a sacrifice.
Back in February it felt like the virus was just China’s problem. And quite a few analysts in the West were saying: ‘you know, this virus, it could be China’s Chernobyl, the CPC is going to lose its popularity, it’s going to lose its legitimacy, because of the pandemic’. Is that what happened?
Probably this is going to disappoint a lot of Western politicians, but it made the people here, trust and love the government even more, this outbreak. Maybe in the beginning, it was chaotic. There was a tendency of some people who were just not satisfied with what the governments were doing. But I think it quickly stopped, once they realized that it was a brand-new unknown pneumonia and even the doctors and nurses didn’t know how to deal with it. And the question was: ‘Should we put on a lockdown? How do we provide necessities to people?’ But as soon as they figured out how serious it was, and how it was transmitted between people, all the methods were put in place quite fast and quite effectively. When the lockdown was announced on January the 23rd, it was just two days before Spring Festival, and the lockdown was put in place, right on time. After that the people had a lot of trust in the government and the CPC.
I guess one of the things that you hear on Twitter, is people saying: ‘Oh, well, China’s just lying about the statistics, they haven’t really handled the pandemic at all. They just made up the numbers’. What’s your response to this?
Infectious disease is something you cannot hide. China in their eyes is just inferior. They cannot accept that China is doing much better than the superior Western democracy. But if they don’t trust it, let them take a look at our life. What are we doing? We are partying, we are travelling everywhere, our economy is growing. We’re probably the only country where the economy is growing now. So that’s the reality. And then about the numbers. I know there are a lot of people with doubts about the numbers on Wuhan. I was there and interviewed a patient. His parents died in early February. And because it was so early, and it was chaotic, his parents were not listed. But he told me, during the two months into the pandemic, he got a lot of calls from different departments of local communities, government hospitals, everywhere, constantly checking, asking the information on his parents. And I asked him: ‘well, in the beginning, your parents were not counted in the numbers. Were you frustrated by that?’ And he said: ‘No, I totally understand because it was so chaotic. In the beginning, all the doctors, all the nurses were busy saving patients, those who still have the chance to live, and community workers were saving people locked into their apartments by delivering food, so it’s understandable that they didn’t have the time to count who precisely died of COVID-19’.
I hope everyone’s learning that international cooperation is extremely important to address this pandemic, and also future public health crises. How has China been helping other countries to cope with the pandemic? And related to that, in what ways did other countries help China during the crisis in Wuhan?
I think according to the official information, China already helped 83 countries to fight this pandemic, donating masks, test kits, or intubation machines or whatever. I think America was among those 83 countries as well. And they already sent medics to several countries as well, doctors who had already got the first experience in Wuhan of how to deal with this. And during the crisis, there were so many countries helping China as well, either by donating masks, or donating food. I remember Japan also showed quite a lot of support. So during that time Japan-China friendship got so much better during the worst time, the people who showed you support are the ones that you know are your true friends. And you’re going to remember forever.
Now, the Chinese vaccines are starting to be rolled out. And there’s clearly a big focus on developing countries. Also, the Chinese vaccines are much cheaper than the high profile, western ones. And because of that, the big story in the Western media is suddenly ‘vaccine diplomacy’. Do you have any opinion on that?
It’s always the same: first, it’s panda diplomacy, then it’s mask diplomacy. Now, it’s vaccine diplomacy. So no matter what you’re doing, when you are doing something good people are still going to judge you. I remember when, during the worst time in Wuhan we needed masks the most and the masks expired every few hours. We didn’t have enough for all citizens. In China we have a large population, 1.4 billion. So China stopped its export of masks and the sale of certain medical resources to other countries. And I remember some media were criticizing China for this. Finally we had enough and were able to help other countries. The government realized we can help other countries which are needing it now, because it is getting worse. So they decided to help other countries. We were helping them and they still judged us. But well, we don’t care what they’re saying. Because helping other countries and people in desperation is the right thing to do. We had been through that worst time so we knew how it felt: as if the world was coming to an end.
You monitor the Western media, you have probably seen there’s been a lot of racist anti-Chinese sentiment generated particularly by right wing politicians in the West, who want to blame China for their own failure to contain the Coronavirus. Do people in China see this? Do they talk about this? What do you know about their opinions about this?
I think most Chinese know that. It’s quite frustrating. We have so many international students in other countries. Many Chinese work in other countries, and they are living through a tough time. But also those Asian descendants that were born in America, in Britain also get discriminated against. Very unfair and sad. Do you really have to blame a whole race, or whole nationality for a certain disease? The first AIDS patients were detected in America. Did anyone blame the whole of America for AIDS? Did anyone blame America or Mexico for H1N1? It’s not right.
Anything that makes China look good or makes China seem attractive, especially as a socialist country, especially as a country that’s run by a Communist Party, especially as a non-white country as well, is considered a big challenge. And you know, it’s very predictable and almost inevitable that there’ll be some racism connected with that sentiment.
You’ve lived in the West. Do you have any advice? What do you think other countries, especially countries in the West can learn from the way that China has managed the pandemic?
I don’t think other countries need to exactly copy everything China does, because every country has their own situation, their own culture. What may be very useful is going from door to door to really check everyone, categorizing into four different kinds of people: confirmed patients, suspected patients, close contacts, and patients with a fever, provided with four different treatments. Some patients will be sent to hospitals, hospitals with ICUs, and mild symptom patients sent to makeshift hospitals, and fever patients and close contacts will be sent to quarantine centres. They will be treated well and they won’t overwhelm the medical system. You cannot let close contacts and fever patients stay at home, because they’re going to infect more people there. During the quarantines, they’re going to test those people four times. That’s the way to stop this transmission chain. And also for the food and groceries. I think some countries will probably think about their own plans. You have to deliver food, medicines and medical care to different households during the lockdowns. If you just leave people at their homes without providing any help, they’re going to die, not from COVID-19, but from other things. The third thing I think most important is: just unite. As long as we all pull together this thing can be conquered. In terms of the doctors and medics in Wuhan: seven times they upgraded their diagnosis and treatment schemes. The city, the government, the medical staff, they are always updating based on the information they have got. It took them three months. Other countries have already been seeing this for almost a year. Why are they not upgrading their methods, their solutions?
I can definitely relate to that here in Britain. You can’t get tested unless you pay privately for it, or unless you’ve got symptoms. And then I know people who tried to get tests, and they look on the app to see where they can go. And they’re being asked to go like 100, 150 kilometres to the nearest available test centre.
During the whole outbreak in Wuhan, nobody had to pay anything. They didn’t have to pay for the treatment they got in the hospital, no matter what that treatment was. They found five cases in one district and they tested 1 million people in that district without asking for any money. Because that’s needed. Those close contacts and fever patients who were sent to quarantine centres did not have to pay for the accommodation or the food. I think the government covered all the other costs. So the patients were willing and able to go to those places. Many patients were migrant workers , none of them had to pay. When they were discharged from hospital they were crying and saying: ‘you really saved our lives. Without this kind of hospital, I would just die probably on the street or at home’. I think what China did was really great. You will find that when you ask anybody.
Li Jingjing, I want to thank you for giving us a lot of your time, for sharing your experiences which has been really fascinating, and I hope it will provide some useful ideas for other people watching.
Thank you, thank you for having me here. I would love to help more people. Because I saw probably the worst outbreak in Wuhan. The knowledge we got is precious and, I think, useful for other people who are still suffering from this pandemic. We would like to help people in need.